The mathematical model relies on a switching function
![]() that depends on a priori
values
that depends on a priori
values ![]() and a posteriori
values
and a posteriori
values ![]() .
The semantics are specified by
the recursive relation between
.
The semantics are specified by
the recursive relation between ![]() and
and ![]() which takes the form
which takes the form
Note the ![]() subscript in
subscript in ![]() .
If
.
If ![]() is independent of
is independent of ![]() ,
this results in the general sequence
,
this results in the general sequence
In this sequence, each mode, ![]() , may be departed when any of the
three assignment statements is executed.
In the model in
Fig. 2b this corresponds to additional feedback of
, may be departed when any of the
three assignment statements is executed.
In the model in
Fig. 2b this corresponds to additional feedback of ![]() into
into ![]() which introduces a loop between g and
which introduces a loop between g and ![]() .
Overall, three cases can be distinguished (Fig. 6):
.
Overall, three cases can be distinguished (Fig. 6):
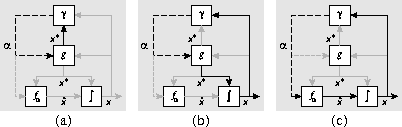
Figure 6: Classes of modes of operation.